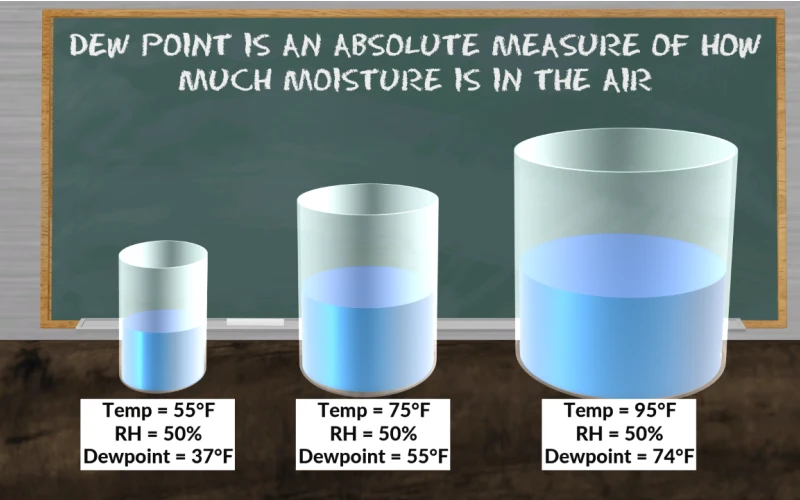
。
html
How is Dew Point Calculated?
The dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor, leading to condensation. Calculating the dew point is essential in meteorology, HVAC systems, and industrial processes. Here’s how it’s determined.
Basic Formula for Dew Point Calculation
The dew point can be calculated using the Magnus-Tetens formula, which approximates the relationship between temperature, humidity, and dew point:
Td = (b × α(T,RH)) / (a – α(T,RH))
Where:
- Td = Dew point temperature (°C)
- T = Air temperature (°C)
- RH = Relative humidity (%)
- a = 17.27 (constant)
- b = 237.7 °C (constant)
- α(T,RH) = (a × T / (b + T)) + ln(RH/100)
Step-by-Step Calculation
To compute the dew point manually:
- Measure the air temperature (T) and relative humidity (RH).
- Calculate α(T,RH) using the formula above.
- Plug the result into the dew point equation to find Td.
Example Calculation
Suppose the air temperature is 25°C, and the relative humidity is 60%:
- Compute α(T,RH):
α = (17.27 × 25 / (237.7 + 25)) + ln(60/100) ≈ 1.313 + (-0.511) ≈ 0.802
- Calculate Td:
Td = (237.7 × 0.802) / (17.27 – 0.802) ≈ 190.6 / 16.468 ≈ 16.57°C
Thus, the dew point is approximately 16.6°C.
Alternative Methods
Besides manual calculation, dew point can be determined using:
- Psychrometric charts – Graphical representations of air properties.
- Online calculators – Tools that automate the formula.
- Dew point meters – Instruments that measure it directly.
Why Dew Point Matters
Understanding dew point helps in:
- Predicting fog or frost formation.
- Optimizing HVAC efficiency.
- Preventing moisture damage in industrial settings.
By knowing how to calculate dew point, professionals and enthusiasts can make informed decisions about weather, comfort, and equipment performance.
Keyword: how is dew point calculated